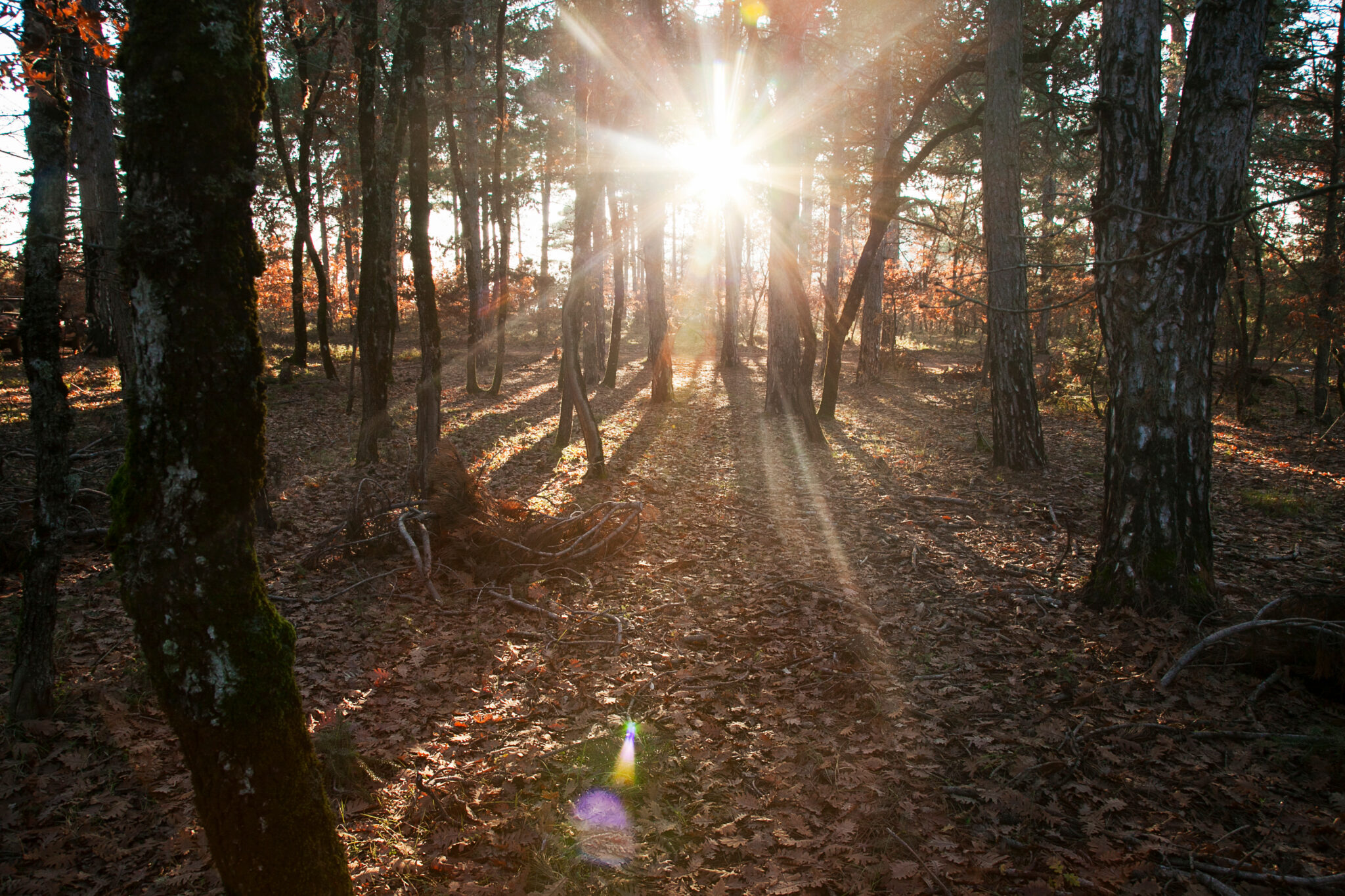
The largest and by far the most famous oak forest in Greece is that of Foloi, in the mountains of Ilia. Another, much smaller, forest where the oak tree also prevails is located in the Peloponnese. It is the forest of Moggosto, at altitudes of 700-930 meters on the slopes of Mount Ziria in Corinthia. The forest covers an area of just over 7,000 stremmas, of which 5,200 are protected as an “aesthetic forest” since 1977 and today are included in the NATURA network.
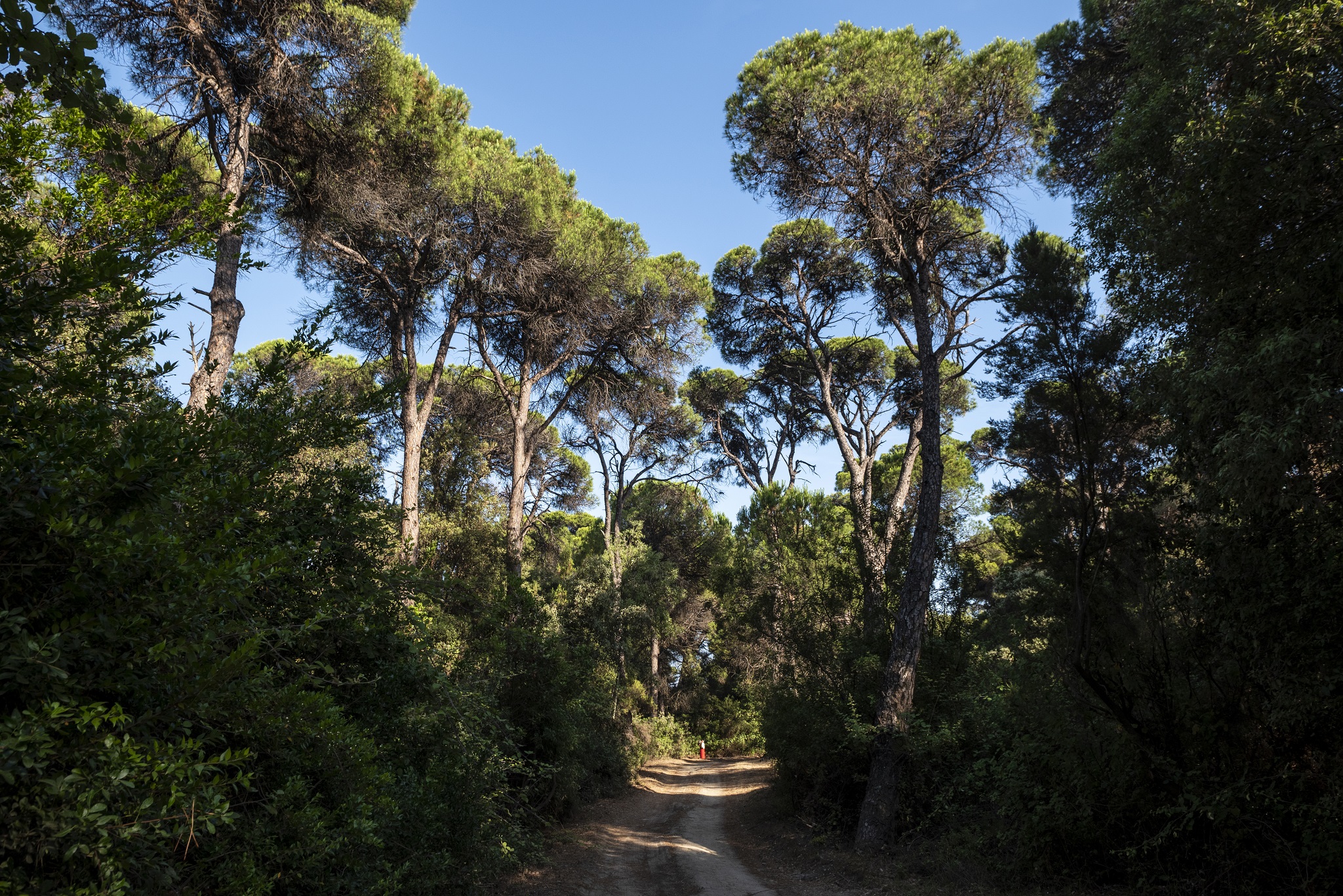
The forest is located between Throfari, Megalos Valtos, and Souli villages, the latter being built at an altitude of 620 meters and offering a magnificent view of the Corinthian Gulf. The forest itself is highly recommended for gentle hiking excursions as it has a network of forest roads and trails that are in good condition.
For this reason, it is a popular choice among nature and hiking clubs from the wider area. Apart from the broad-leaved oak that defines Moggosto with the designation of “oak forest,” other trees and plants found here include the black pine, Aleppo pine, heather, arbutus, and various species of wildflowers.
The Moggosto Oak Forest, like the much larger Foloi, is one of the remnants of the ancient oak forests of the Peloponnese. They are small visible samples of how different the flora (and fauna) of Greece was in periods when the concept of “climate change” didn’t exist. The forest may have been one of the many places in the Peloponnese where lions lived during the Prehistoric Period, which “created” the mythical “Nemean lion”. Certainly, the forest in Corinthia offers a wonderful day trip experience away from the hustle and bustle of Athens, especially as the temperature rises, provided visitors show respect for the ancient oaks and the other trees.

What is an aesthetic forest?
As mentioned, this forest is one of the 19 aesthetic forests in Greece, covering an area of 325,000 stremmas. According to the Forest Code of 1971, an aesthetic forest exhibits the characteristics of a National Park, holding particular aesthetic, health, and touristic significance. In the protection status that identifies a natural or artificial forest, its quality as a place of human recreation is emphasized due to the beauty of the landscape and its other characteristics. This does not mean that the protection of the natural environment is not of interest or that rare species of birds and animals cannot live within the forest.
The Other 18 Aesthetic Forests:
Vai Palm Forest
Kaisariani Forest
The Valley of Tempi
Karaiskaki Forest in Karditsa
Xylokastro Pine Forest
Suburban Forest of Ioannina
Forest of Selimno Streams and Gorges, Panachaiko Mountain
Farsala Forest
Steni Evia Forest
Ossa Forest of Larissa
Forest of Nikopoleos Preveza
Skiathos Forests
Nestos Straits of Kavala – Xanthi
National Independence Forest, Kalavryta
Tithorea Forest
Almond Forests of Kavala
Ailias Forest of Trikala
Kouri Oak Forest, Magnesia
Top Tips for Your Visit
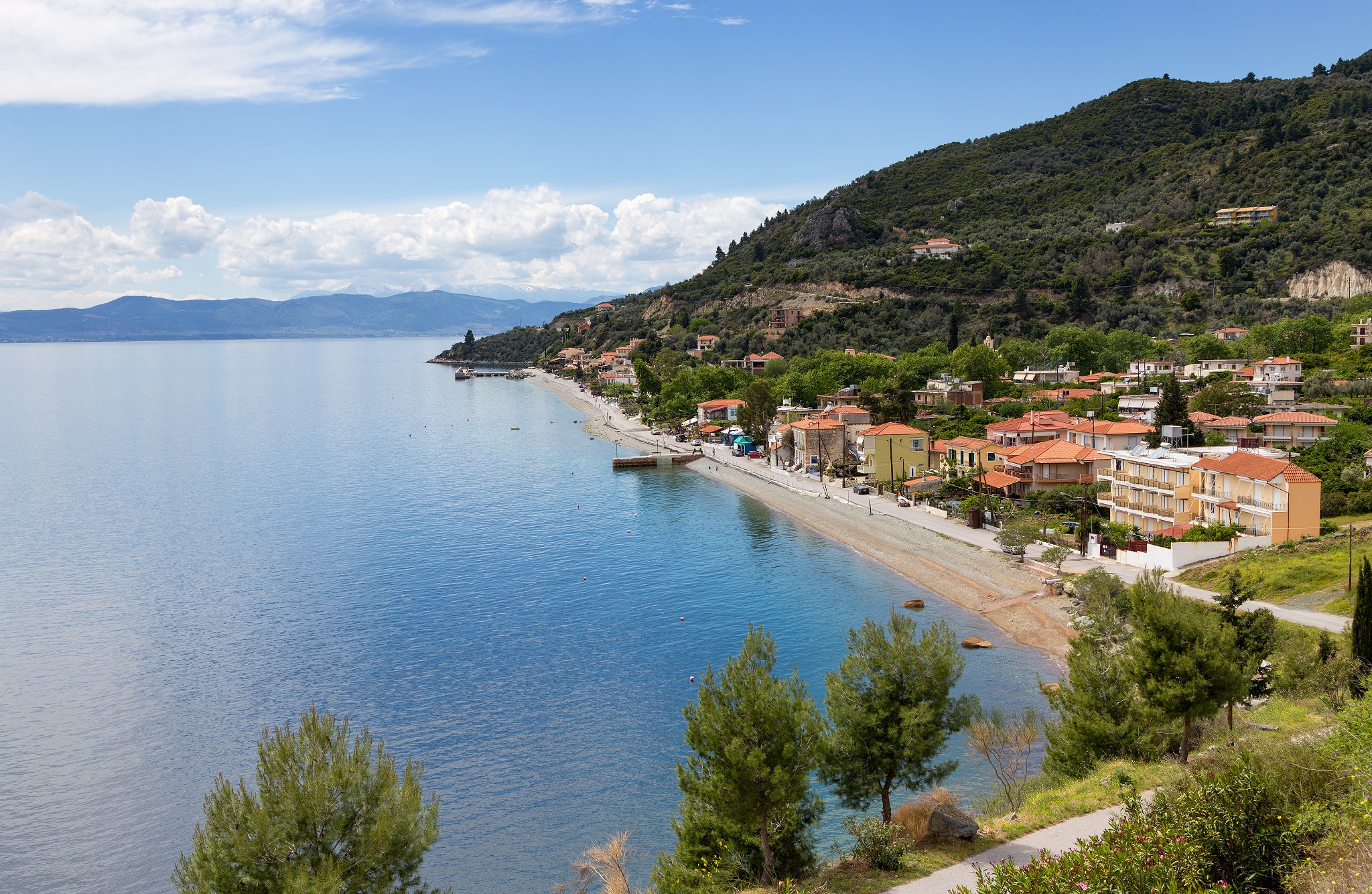
The Moggosto Oak Forest is approximately 120 kilometers from Athens. It lies around 122 kilometers from Patras and about 45 kilometers from Corinth.
The forest can be part of a nature-loving trip with an educational character, which should include a visit to Lake Stymphalia and the Environment Museum. There, you’ll get better acquainted with the flora and fauna of the area.
During the summer months, a good complementary choice is Xylokastro with its long beach, a part of which stretches in front of a large pine forest.
Read also:
Mission to Trikala of Corinthia, mountainous paradise 150km from Athens
A day in Acrocorinth, the imposing fortress of the Peloponnese